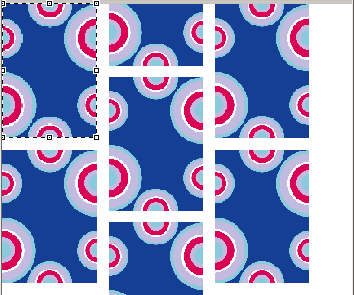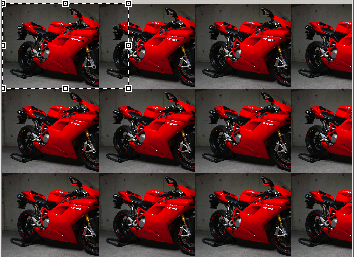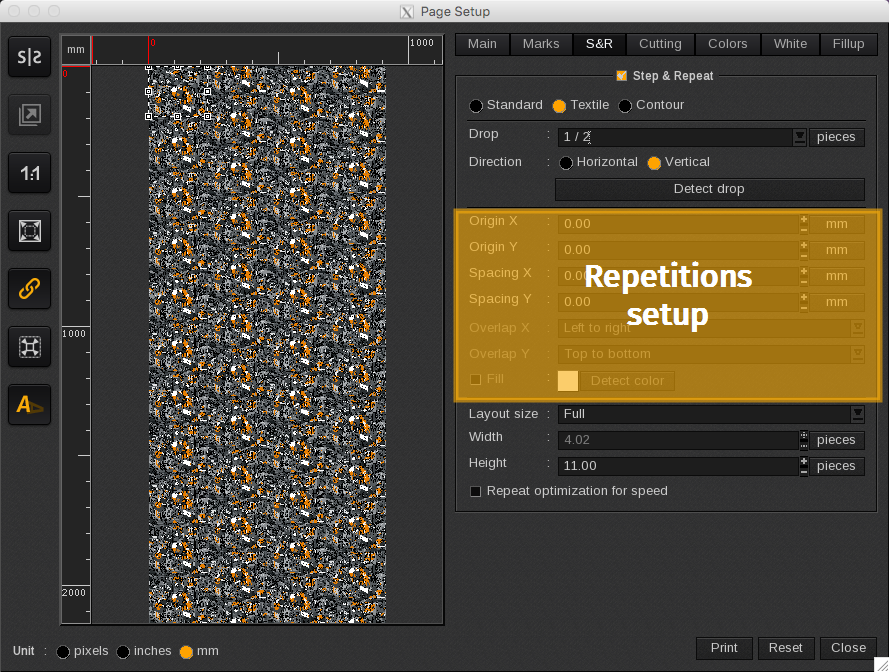
The page setup allows to move forward the image origin and to define spacing and overlap procedures.
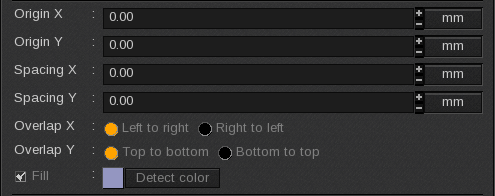
Image origin
The image origin can be moved forward on the page. This move is indicated in number of pieces or in distance (either in pixels, inches or millimeters depending on the unit chosen for the page configuration tools). By default, origins are fixed at 0.00.
The origin has to be chosen between -1 and 1 piece. It is recommended not to use a negative origin. A 1 X and 1 Y origin displays the image as if no move has been made.
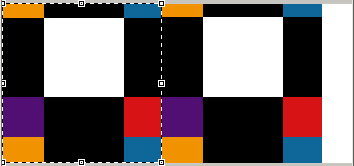
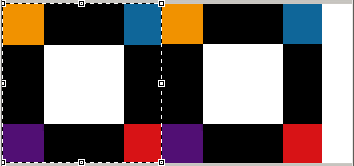
Origin move examples. The image drop is 1/1. On the original place, the white square is center.
 |
 |
|
Original position
|
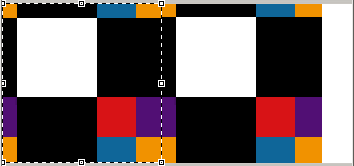
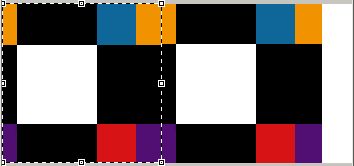
X origin moved (+70mm). Copies are impacted at the right of the line.
|
|
|
|
|
Y origin moved (+70mm).
|
X and Y origins moved (+70mm).
|
Spacing
In Spacing fields, numbers can either be positive or negative. When positive, a space appears between the copies that can be filled. When negative, an overlap is created.
By default, no spacing is specified.
Be careful, the piece size calculation takes the spacing into account. A piece is the image size + the spacing.
The piece size has influence on the drop calculation and the size of the document.
Filling
A positive spacing moves the repetition right (X) and down (Y) creating some space between the copies.
Positive spacing examples:
|
|
|
|
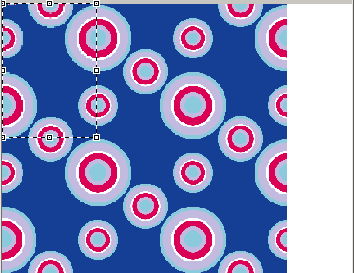
Original position
|
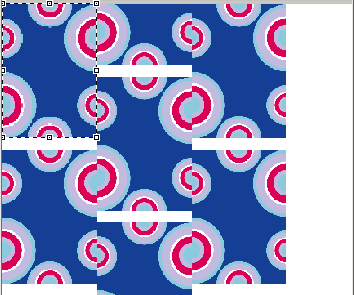
X spacing (+30mm).
|
|
|
|
|
Y spacing (+30mm).
|
X and Y spacing (+30mm).
|
By default, the space generated is considered as an unprinted area. It is possible to fill this space with color.
To fill the space, the box has to be checked:

Clicking on the colored square opens the following pop-up to change the color:
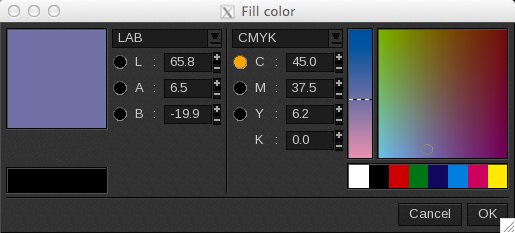
The color modes available are LAB, HSV, XYZ or CMJN, RVB, and Grey.
The Detect color button allows the user to let the system choose the proper color to fill in. The image border color will be detected and applied or, if the image has multiple border colors, an average value will be calculated.
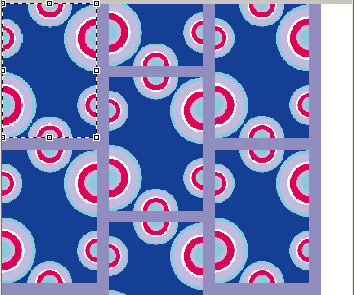
The color used to fill the space has been calculated with the detection color button.
Overlap
A negative spacing moves the repetition left (X) and up (Y) creating an overlap between copies.
The overlap principle can be defined according to:
- The X axis:
- Left to right: the left copy is over the right one.
- Right to left: the right copy is over the left one.
- The Y axis:
- Top to bottom: the top copy is over the bottom one.
- Bottom to top: the bottom copy is over the top one.
When there is an overlap on the X axis and on the Y axis, the X axis makes its move first then the Y does (see last example).
Overlap examples:
The chosen image is not relevant for textile printing. This choice has been made to have a better vision of the overlaps.
|
Original position
|
|
||
|
X spacing (-80 mm).
|
Left to right
|
Right to left
|
|
|
Y spacing (-80 mm).
|
Top to bottom
|
Bottom to top
|
|
|
X and Y spacing
|
Left to right and top to bottom.
|
||